OVERVIEW
The High-Availability cluster and the Cluster
Resource Manager are responsible for the recovery of nodes in case of
failure in the network occurs. The concept of Active and Passive
Cluster will be discussed in this activity.
Active/Passive
Cluster
The Active/Passive Cluster works when a
node (active node) fails, the passive node will assume the role of the failed
node, and the service will continue.
Two computers (servers) are needed in this cluster. One
computer will serve as the active node, while the other is the passive node.
Once the process execution of the active node fails, the passive node will take
over of the execution, so that the failure will never occur.
 |
| Active/Passive Cluster |
PROBLEM
STATEMENT
The activity needs to be performed by at least two people.
Two to three computers are needed to execute the activity. The concept of IP
configuration will be of help because assigning IP addresses and names to each
computer is needed, and a virtual IP address to a computer that will act as a
server. The Active/Passive Cluster will be use.
GUIDES
IN SOLVING THE PROBLEM
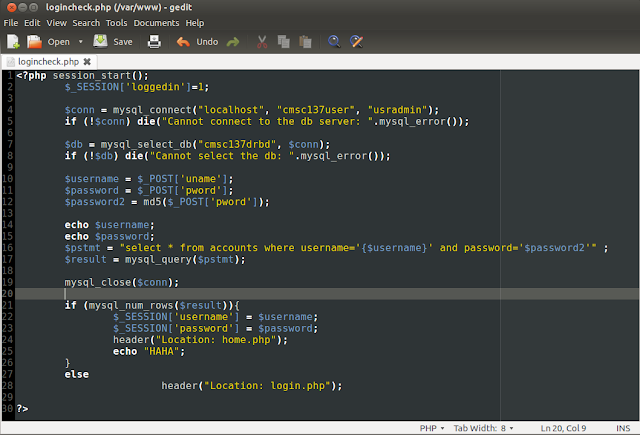
Configuring
the needed configuration files
To be able to configure two servers using Apache and
Heartbeat to communicate with a client or browser, we need to edit several
configuration files. And these configuration files are as follows:
- ha.cf
- authkeys
-haresources
The haresources file can be found at
/etc/ha.d directory. It contains the name of the server assigned to be the
active node, and the virtual IP address needed.
 |
| Edit haresources file |
- /etc/hosts
The /etc/hosts file should contain the name
of the two computers which will act as the two server with its distinct IP
address. Also, the virtual IP address or alias of another server holding the
said two servers should be specified along with its name. To edit this file,
type $ sudo gedit /etc/hosts.
 |
| Edit /etc/hosts file |
- /etc/hostname
The /etc/hostname file should contain the
name of the computer you are using. It is neccessary for the ha.cf and
/etc/hosts files.To edit this file, type $ sudo gedit /etc/hostname.
 |
| Edit /etc/hostname file |
Test
the Active/Passive Cluster
Try the following commands to test your set-up:
- Check if Apache is running.
Command: $
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
 |
| Start Apache |
- Check if Heartbeat is running.
Command: $
sudo /etc/init.d/heartbeat restart
 |
| Restart Heartbeat |
- Try to access the virutal IP address (10.0.5.66) in the
browser using another computer. It should display the web page of the active
node (server1).
 |
| Web Page of server1 (Active Node) |
- Disconnect the LAN cable of the active node (server1).
Refresh the web page. It should display the web page of the passive node
(server2).
 |
| Web Page of server2 (Passive Node) |
LEARNING AND INSIGHTS
Configuring
the configuration files is a bit challenging because we didn't know how to do
it. Thanks to the power of the Internet, we were able to do it (barely).
Through
patience, we were able to start heartbeat successfully. Also, we were able to
access the active server via the virtual IP address. And if we disconnect the
LAN cable of the active server, the browser can display the page of the passive
server. We were so overwhelmed that we were able to do this after two lab
meetings. T__T
***Lesson
learned (for me): In order to avoid problems, the server
should be regularly restarted so that changes can be made on the server.
CONCLUSION
The activity, for me is so difficult. It is difficult to accomplish because once you have made mistakes on the configuration files, you need to check all those files and trace what was wrong. Though it is kinda confusing, we were able to fulfill the tasks needed in this activity. We barely surpass the trial and error on all the computers in the laboratory to have a better access on our virtual server.